|
|
Before booking your shipment, use the online freight calculator above to estimate international shipping costs quickly. It's a fast, straightforward way to get started with shipping from the USA, especially if you're sending cargo to Australia, New Zealand, or other Oceania destinations.
Fumigation Certificate for Shipping from the USA to Australia and New Zealand
If your cargo is bound for Australia or New Zealand, there's an important biosecurity export requirement you can't overlook: mandatory seasonal pest mitigation. These countries enforce strict sea freight quarantine regulations to stop the spread of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (BMSB)—a destructive agricultural pest. If your shipment doesn't meet these international biosecurity standards, it won't be permitted to proceed.

This applies to all international ocean freight services moving freight to, through, or transiting either country, and similar quarantine rules are enforced across parts of Oceania as well.
Seasonal BMSB Treatment Requirements
During the BMSB risk season, from September 1 to April 30, any cargo from the U.S. to Australia or New Zealand must undergo certified chemical treatment. These export protocols apply regardless of whether your shipment is commercial cargo or shipping personal effects.
Before the cargo is loaded for international shipping, your ocean freight carrier must receive a copy of the official treatment certificate. Upon arrival, the original certificate will be required for Customs clearance and quarantine inspection. No valid certificate? No cargo release.
To ensure you're meeting the latest import compliance requirements, it's best to check the official resources:
- For Australia, visit the DAWR website
- For New Zealand, visit the MPI site
BMSB Treatment vs. ISPM15: What's the Difference?
It's easy to confuse mandatory seasonal treatment with ISPM15 wood-packing rules, but they're not the same.
ISPM15 applies to all shipments leaving the United States that use heat-treated wooden pallets, crates, or dunnage. These items must be stamped with a certification mark.
BMSB treatment, on the other hand, is mandatory only for shipments to Australia and New Zealand during the risk season. It applies to the cargo as a whole, not just the packaging.
If your goods aren't properly treated as required, your carrier won't load your shipment. And since global cargo transportation companies must comply with the destination country's biosecurity laws, they can't make exceptions. The responsibility rests with you as the shipper.
The Treatment Options and Costs
To simplify the process, many freight consolidators now offer on-site biosecurity services directly at their container freight station (CFS) terminals. Here's how it typically works:
- The treatment is performed before loading or at a transshipment seaport.
- Service cost is about $30 per weight/measurement (w/m).
- There's a minimum fee, usually $200–$300, depending on the carrier.
The benefit of using the carrier's integrated treatment service is that it's already included in your total international shipping cost, and the carrier assumes responsibility for regulatory compliance. If something goes wrong, the liability is theirs, not yours. This makes it a reliable choice for those looking for affordable sea freight without compliance headaches.
What If You Arrange Treatment Yourself?
You're allowed to handle the pest mitigation on your own, but be cautious. If you choose this route, you'll need to:
-
Provide a copy of the fumigation certificate before delivery to the CFS.
-
Present the original certificate for Customs clearance upon arrival.
Ensure your provider is certified and that the document is correctly formatted. If the certificate is rejected or missing critical information, you could face:
-
Fines of over $1,000.
-
Extra fees for re-treatment or storage.
-
Cargo delays, returns, or even destruction.
That's why using your international shipping company's built-in biosecurity option is often the safest route.
A Real Example: Why It Matters
Here’s an actual case from a shipment to Australia:
"The official certificate had some mistakes. We finished the treatment process over the weekend, and Quarantine finally cleared the container today. You should be able to unpack and pick up the cargo in a day or two. Just a heads-up: the freight won't be released until the charges are paid."
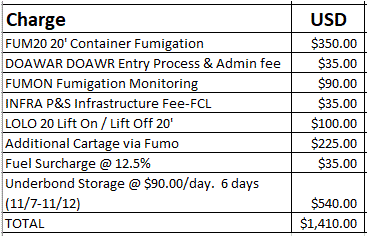
In this case, errors in the paperwork delayed clearance and resulted in additional fees. It serves as a reminder to meet biosecurity requirements before cargo departs the United States.
Summary
If you're shipping from the USA to Australia or New Zealand, pest treatment is not optional - it's a legal requirement. Whether you're working with an experienced global cargo transportation company or arranging everything yourself, be sure to:
-
Know the BMSB season dates.
-
Choose a certified treatment provider.
-
Budget for the added international shipping expenses.
-
Double-check your paperwork to avoid delays.
Proper planning can help you stay compliant, avoid fines, and enjoy smoother, more reliable international shipping to Oceania.
Frequently Asked Questions: Shipping to Australia & New Zealand
1. When is BMSB treatment mandatory for shipments to Oceania?
Seasonal biosecurity measures apply to all cargo departing from the USA between September 1 and April 30 each year. During this window, goods manufactured in or shipped from the U.S. must undergo certified pest mitigation to prevent the spread of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug.
2. How much does a fumigation certificate cost?
While prices vary by ocean freight carrier, the standard service fee is typically around $30 per weight/measurement (w/m). Most consolidators charge a minimum of $200 to $300 to cover the cost of the chemical application and the issuance of the official treatment certificate.
3. What is the difference between ISPM15 and BMSB fumigation?
ISPM15 is a global wood-packing regulation that requires heat-treated wooden pallets and crates to be stamped year-round. In contrast, BMSB requirements are seasonal biosecurity protocols specific to Australia and New Zealand that apply to the entire cargo (including the goods themselves), not just the packaging.
4. Can I arrange my own pest treatment for my cargo?
Yes, shippers may use a private certified treatment provider. However, you must provide a digital copy of the fumigation certificate to your freight forwarder before the cargo arrives at the terminal. If the paperwork is incomplete or the provider is not registered with DAWR or MPI, you may face fines exceeding $1,000.
5. Does air freight require a fumigation certificate?
While the strictest quarantine regulations target sea cargo, both Australia and New Zealand conduct random onshore inspections for air freight arriving from the USA during the risk season. To avoid potential delays or re-treatment fees, many shippers choose to treat high-risk goods regardless of the transport mode.


.png)


